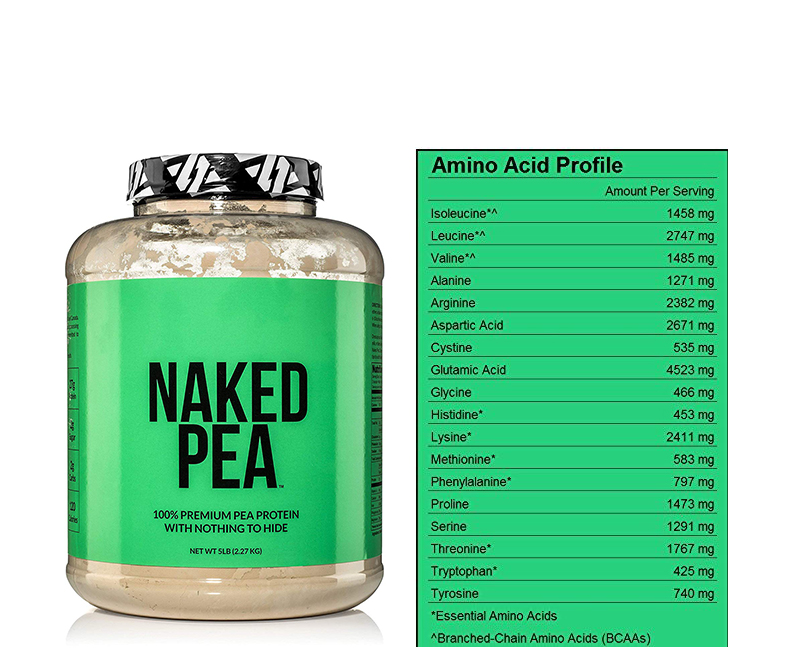
Ingredients called “protein” on ingredient lists are not proteins.
Beef is “beef,” soy is “soy,” tomatoes are “tomatoes,” and peas are “peas.” Those are the FDA’s “common or usual names” for whole foods. “Pea protein” is made of man-made amino acids manufactured in food processing plants with peas as the starting material. And each and every man-made/manufactured hydrolyzed pea protein will contain the three potentially toxic amino acids* aspartic acid, L-cysteine, and glutamic acid. This is true for every hydrolyzed protein. It may be called “natural,” “organic,” or “raw,” but it will still contain potentially toxic aspartic acid, L-cysteine, and glutamic acid. There are no exceptions. And there are no toxic amino acids in whole protein.
Today, there is a widespread marketing effort to substitute hydrolyzed vegetable protein for real protein, and to expand the use of hydrolyzed proteins in general. While there certainly are other varieties of hydrolyzed vegetable proteins, pea protein is presently the favorite of food manufacturers.
Substituting vegetables for meat may have many benefits for consumers, but hydrolyzed vegetable proteins don’t deliver vegetables. What they provide are arrays of amino acids which are produced in food processing and/or chemical plants. And three of those amino acids (L-cysteine, aspartic acid, and glutamic acid) can be toxic to humans. These three amino acids are called “excitotoxins” by scientists. When consumed in amounts that exceed what a human needs for normal body function, they cause brain damage, endocrine disorders, and observable reactions such as asthma, migraine headache, a-fib, fibromyalgia, and seizures. Glutamic acid is the amino acid in MSG that causes brain damage, endocrine disruption, and adverse reactions.
Manufacturers’ claims of benefits for manufacturers
1) Hydrolyzed vegetable proteins are making great inroads into health and nutrition markets.
2) Every hydrolyzed protein will have flavor-enhancing properties. Glutamic acid, the amino acid that triggers taste buds to cause increased perception of taste, will be found in all hydrolyzed proteins.
3) Clean labels are certainly at the top of the list. Unfortunately, not all consumers have caught on to the fact that glutamic acid (a.k.a. glutamate), which is the toxic component of MSG, will be found in all hydrolyzed proteins. So while more and more consumers are attempting to avoid MSG, substituting a flavor-enhancing hydrolyzed vegetable protein for flavor-enhancing MSG would allow the product to have a “clean label” – one that would give the consumer no clue that it contained glutamate, MSG’s toxic component.
4) Hydrolyzed vegetable proteins will have great appeal for vegetarians, vegans and others who want to limit their intake of meat.
Manufacturers’ claims of benefits for consumers (which will also benefit industry)
1) Protein-rich, non-animal products are in great demand as more and more people look for substitutes for meat, fish, and poultry. Hydrolyzed proteins contain the arrays of amino acids that make up most proteins. So, properly promoted, hydrolyzed protein products will appeal to those looking for vegetarian or vegan sources of dietary protein. The fact that high-protein diets are being touted for weight-loss, makes these products even more attractive.
2) Chemical-free claims are another way the food industry is hyping hydrolyzed proteins. Although all hydrolyzed proteins are produced in food processing and/or chemical plants, industry’s promotional materials refer to hydrolyzed vegetable proteins as being “natural” – saying they are derived from a variety of “natural plant resources.”
That should be no surprise since MSG, which is made by fermentation of carefully selected genetically engineered bacteria that secrete glutamic acid through their cell walls, is referred to by industry as “naturally occurring.”
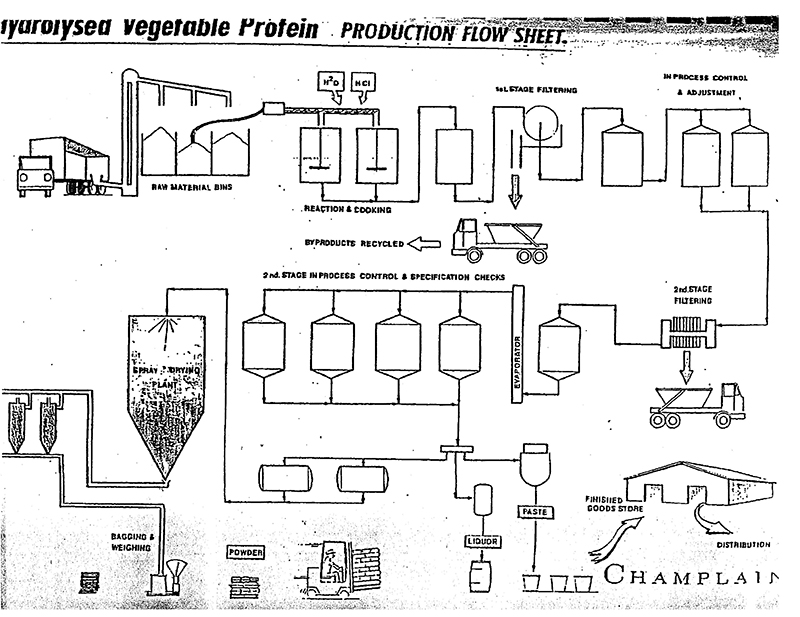
3) Claims of health benefits from hydrolyzed vegetable proteins are typically made. Market-watchers claim that consumer awareness of these so-called benefits is increasing. The claim has been made that hydrolyzed vegetable proteins will help reduce intake of saturated fat and cholesterol, and because it’s an effective way to lower cholesterol, it will decrease the risk of heart disease.
But even with all that propaganda going for it, something is still bothering the glutamate industry.
You’d think that with all their research and planning, glutamate industry giants would feel secure in their efforts to sell hydrolyzed proteins to naïve consumers. But that doesn’t seem to be the case. It would appear that consumers’ growing recognition of the toxic effects of the manufactured glutamic acid in MSG, hydrolyzed proteins, maltodextrin, and some other 40+ ingredients is getting in the way of sales. One industry watcher said it this way, “The high contents of monosodium glutamate (MSG) in hydrolyzed protein products continues to be a bottleneck for pervasive adoption as consumers show an unprecedented alacrity** to read labels to spot ingredients with a bad rep in terms of potential side effects.”
The Truth in Labeling Campaign would like to take some of the credit for that greater consumer awareness and “alacrity.” So, let’s hear it for the Truth in Labeling Campaign — since 1994, providing consumers with the names of ingredients in which manufactured free glutamate, the brain-damaging, endocrine-disrupting, reaction-causing component of MSG, are hidden.
*killing brain cells and disrupting the endocrine system when present in quantity
**enthusiasm, readiness, quickness, promptness, speed, swiftness, rapidity, keenness, zeal
If you have questions or comments, we’d love to hear from you. If you have hints for others on how to avoid exposure to MfG, send them along, too, and we’ll put them up on Facebook. Or you can reach us at questionsaboutmsg@gmail.com and follow us on Twitter @truthlabeling.